Current
Practices in Corporate Video Production
In this essay I will be talking about the laws that
production companies have to follow when producing a corporate video. These
include: contempt, copyright, privacy, defamation, courts, ethical and
finishing off with technologies. I will be looking at a variety of videos that
cover these points.
Copyright:
Copyright is when an individual or company wants to protect something
that they have created material and want to protect them from other people
using it without permission. The creator can control how the material is used,
if a substantial (significant, not quantity) amount of their content is used,
then they get a reward. The works that the copyright laws cover is Literacy,
Musical, Dramatic, Pictorial/Graphic/Sculptural, Motion pictures, Sound
recordings and Architectural. Copyrighted material can be used in certain cases
such as the news and by critics for reviews. Copyright is also a territorial
right so UK copyright abroad is protected and foreign works are protected in
the UK.
https://youtu.be/1DjuUln6xZs
This video is a good example as follows the copyright rules as it just uses
royalty free music so they can use as much of it as they want without getting
any copyright strikes. There are no clips or music that may be copyrighted as
clips in this video are all from frontier airline staff and inside their
airport, so it is all their own works.
Privacy:
Privacy is when the courts will allow people to live a private
and family life over the medias idea of freedom of expression. This law has
developed since the European Convention on Human Rights. Privacy law is
reporting on someone’s personal/sexual live, their finances, information about
their health and filming in their house without permission. Invasion of privacy
is when someone takes to court about their private information being realised
so they want a reward for the level of damages done, the highest award recently
was £60,000 and then the losing party have to pay the legal costs for the
trial.
An example of privacy is when a someone is being filmed and
there is personal information in the shot that someone doesn’t want the public
to know, so that part of the video would either need to be cut or blurred out.
Defamation:
Defamation is the law that allows individuals, companies or
firms to sue is their reputation is damaged by a piece of material that is
published and makes defamatory comments about either of them. Defamation counts
if it: lowers someone in the estimation of right-thinking members of the
public, causes them to be shunned or avoided, disparages them in their office,
trade or profession and/or exposes them to hatred, ridicule or contempt.
An example of defamation is when companies slander each
other and say that one is better compared to the other, another example is when
a newspaper/magazine prints information about someone that they know is untrue
even before they release it to the public.
Fair Use:
Short clips of copyrighted material may, under certain
circumstances, may be used for certain purposes such as criticism, news
reporting, teaching, and research, without the need for permission from or
payment to the copyright holder. The media doesn’t just have to be a short clip
of a video, it can be a small sample of a piece of music or it can be a
screenshot from a video/film/television show etc.

An example of fair
use is in YouTube videos when they use screenshots/clips from a video or film
Ethical Issues:
In corporate videos, ethical issues are when a company,
product or individual may include footage that can offend a certain religion,
ethnicity or individual, or show them in a certain light. These issues can be
used to try and change the outlook that the general public have on a specific person,
culture or religion so that they get targeted by the public as well.
An example of this, is, if a video that was filmed in an
office only had filmed scenes that only included Caucasian male and no one
else, this could mean that the producers being prejudice to woman and other
people of ethical genders.
Release:
Releases are a form of legal permission that need to be
signed by the cast and crew, owners of music used in the production and the
owner of buildings and land that are featured in the video. They must be signed
by these people for the production to start, if they don’t get the permission
or signatures from the people involved filled in then they are not legally
allowed to publish the video with the individuals who have not filled in the form.
An example of this would be, if a corporate video filmed in
a public location such as a train station or a library without getting the
permission from the owners of those locations, then they uploaded the video
onto the internet or wherever they are uploading it without them knowing.
Technologies:
To make a corporate video the production team will need
multiple items that are required for them to finish the entire product, they
include a camera, editing software and any other technological items such as
artificial lighting and microphones to complete the production.
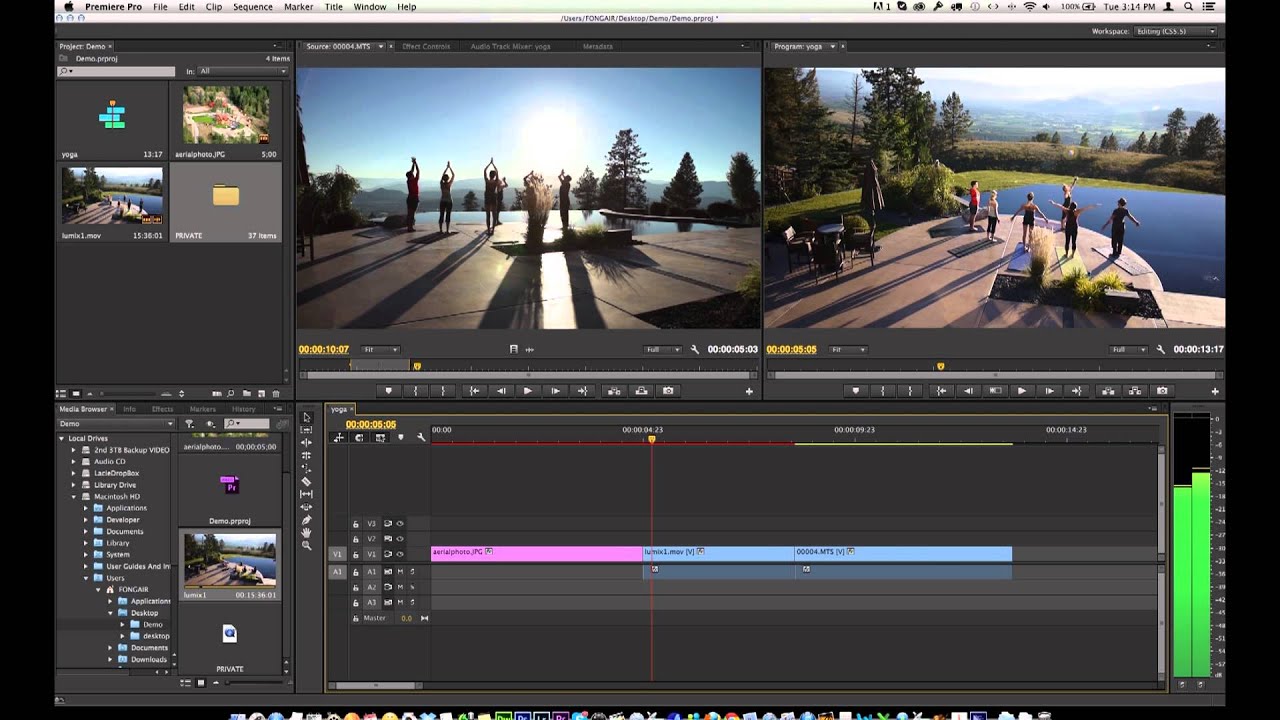
An example of editing software a company might use is Adobe
Premiere Pro CS5.5. This software can support video up to 10,240 × 8,192
resolution, at up to 32-bits per channel colour, in both RGB and YUV. It also
has a 5.1 surround sound mixing and allows the user to import and export
formats that don’t just include QuickTime or DirectShow and supports a wide
variety of video and audio file formats and codecs on both MacOS and Windows.
It can also integrate with the following adobe programs: Adobe After Affects,
Adobe Photoshop and Adobe Story, OnLocation and Prelude.

An example of a Camera that can be used is a Canon EOS
1200D. This camera is relatively cheap for anyone starting off in video as it
only cost a reasonable price of £279.99 and is an easy camera to use, so is
excellent to start off with. This camera has a 18MP sensor compared to the
12.2MP sensor on its predecessor the 1100D, it has a Digic 4 image processor.
It also comes bundled with Canon’s Digital Photo Professional editing software
and also comes with a 28.8-88mm lens.


An example of other essential technologies is a Rode
VideoMic GO Lightweight On-Camera Microphone. This microphone is a good
addition to the camera as it only weighs 2.6 ounces so it keeps the camera
lightweight for easy manoeuvrability and can be kept steady. The mic also only
requires a standard 3.5mm headphone jack so it will be compatible with almost
any camera.


No comments:
Post a Comment